Tutorial
This page demonstrates the Python frontend of Bench-MR.
Construct MPB Instance
The MPB class exposes the settings and several helper functions of an experiment that runs on a single CPU. A single experiment can consist of multiple runs in different environments of the same type, using a set of predefined planners, steer functions, and post-smoothing methods.
from mpb import MPB
mpb = MPB()
The MPB instance is created via the following constructor:
mpb = MPB(config_file = os.path.join(MPB_BINARY_DIR, 'benchmark_template.json'),
output_path = '')
| Argument | Description |
|---|---|
| config_file | Path name of the configuration JSON file this experiment is based on |
| output_path | Path where the resulting log files are stored from this experiment |
Configuration
Any configuration values (or subtrees) can be set and retrieved using the bracket operator on the MPB instance. The key is a string and by using the dot-notation, a path can be given:
mpb["ompl.seed"] = 4 # set the seed of the OMPL planners
Some helper functions are available to set environment properties, and configure the planners, steer functions and post smoothers:
mpb.set_corridor_grid_env(radius = 3)
mpb.set_planners(['rrt', 'rrt_star', 'informed_rrt_star'])
mpb.set_steer_functions(['reeds_shepp'])
Run the motion planning benchmark:
mpb.run(id='test_run', runs=3) # optional run ID, number of runs (environments)
The following command summarizes some basic planning results from these 3 runs that were just executed:
mpb.print_info()
+++++++++++++++++++++++++ Run #0 (1 / 3) +++++++++++++++++++++++++
+ Steering: Reeds-Shepp
+ Environment: grid
+ Planners: RRT, RRTstar, InformedRRTstar
+ Found solution: 3 / 3
+ Exact solution: 3 / 3
+ Found colliding: 0 / 3
++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++
+++++++++++++++++++++++++ Run #1 (2 / 3) +++++++++++++++++++++++++
+ Steering: Reeds-Shepp
+ Environment: grid
+ Planners: RRT, RRTstar, InformedRRTstar
+ Found solution: 3 / 3
+ Exact solution: 3 / 3
+ Found colliding: 0 / 3
++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++
+++++++++++++++++++++++++ Run #2 (3 / 3) +++++++++++++++++++++++++
+ Steering: Reeds-Shepp
+ Environment: grid
+ Planners: RRT, RRTstar, InformedRRTstar
+ Found solution: 3 / 3
+ Exact solution: 3 / 3
+ Found colliding: 0 / 3
++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++
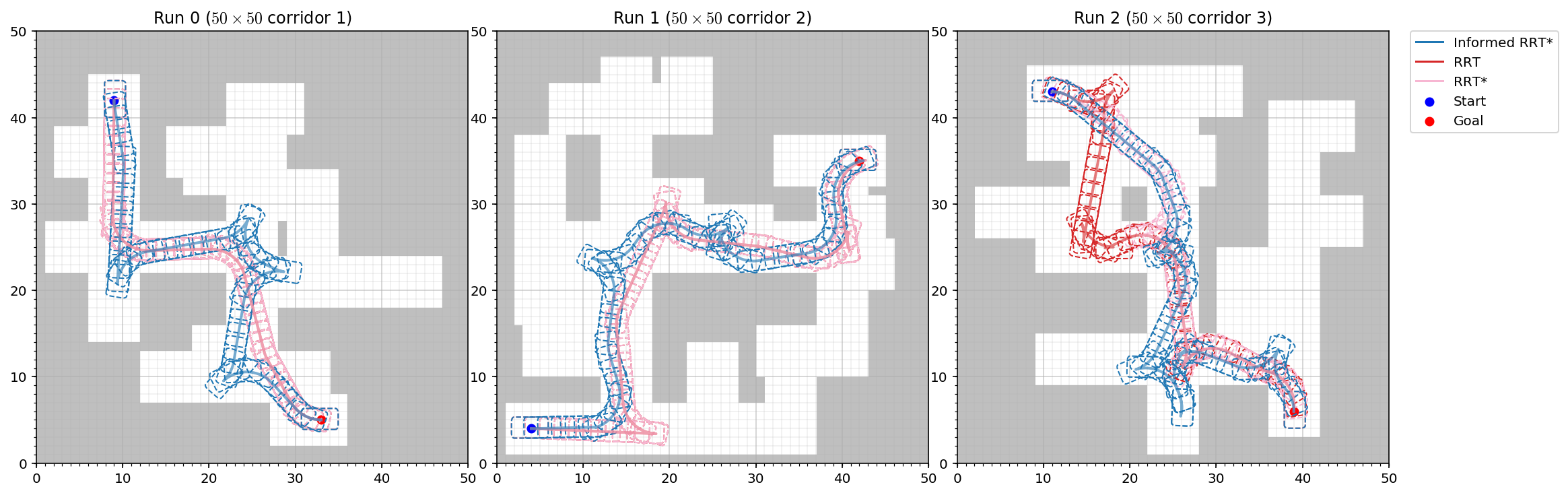
Visualize Trajectories
Visualize the planner trajectories:
mpb.visualize_trajectories()
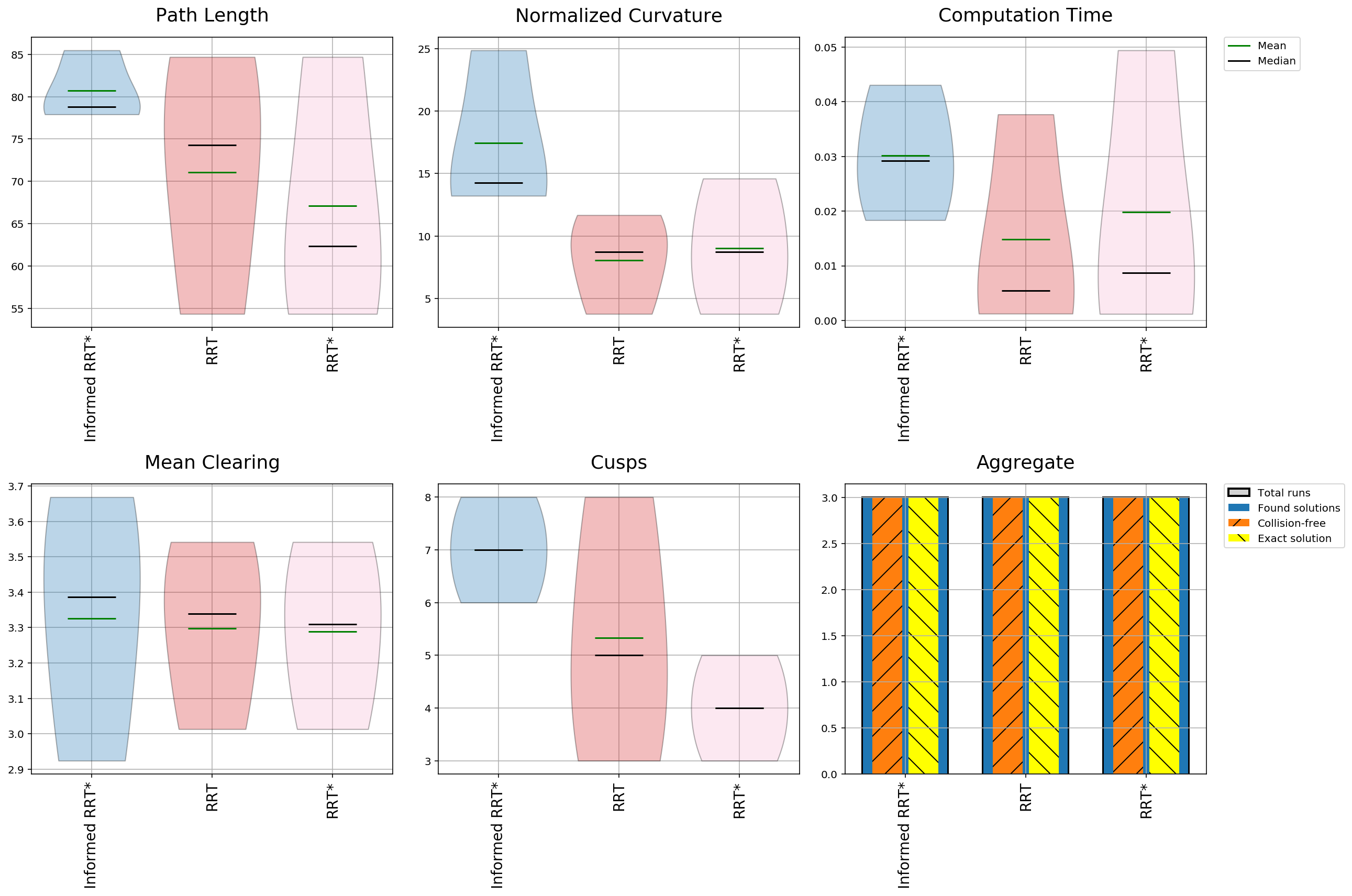
Plot Statistics
Plot planner statistics:
mpb.plot_planner_stats()
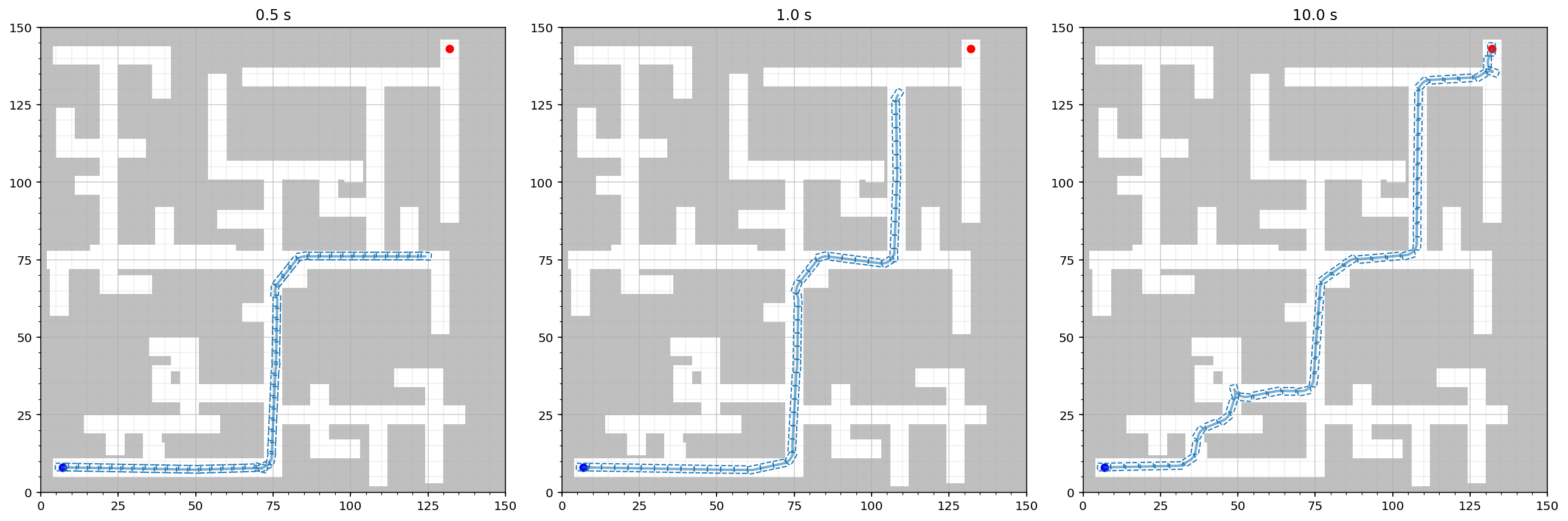
We can also use the frontend to compare the solutions of the anytime planners over the course of a given time interval. Let’s take an Informed RRT* planner and run it on the time allotments of 0.5s, 1s and 10s:
ms = []
for time in [.5, 1, 10]:
m = MPB()
m["max_planning_time"] = time
m.set_corridor_grid_env(width=150, height=150, branches=100, radius=3)
m.set_planners(['informed_rrt_star'])
m.set_steer_functions(['reeds_shepp'])
m.run('anytime_%.1f' % time, runs=1)
ms.append(m)
Visualize the results:
plt.figure(figsize=(6 * len(ms), 6))
for i, m in enumerate(ms):
plt.subplot(1, len(ms), i+1)
m.visualize_trajectories(headless=True, combine_views=False,
use_existing_subplot=True, show_legend=False)
plt.title("%.1f s" % m["max_planning_time"])
plt.tight_layout()
plt.savefig("informed_rrt_star_anytime.pdf")
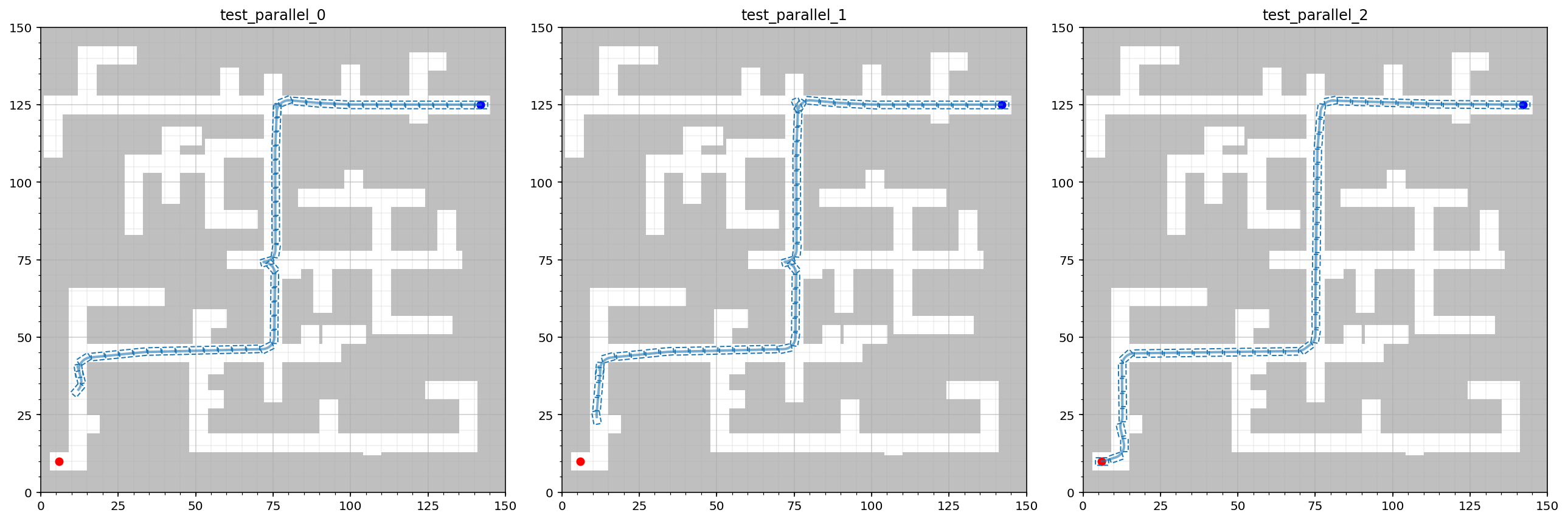
Parallel Execution
Multiple benchmarks can also be run in parallel using MultipleMPB:
from mpb import MultipleMPB
pool = MultipleMPB()
for time in [.5, 1, 10]:
m = MPB()
m["max_planning_time"] = time
m.set_corridor_grid_env(width=150, height=150, branches=100, radius=3)
m.set_planners(['informed_rrt_star'])
m.set_steer_functions(['reeds_shepp'])
pool.benchmarks.append(m)
pool.run_parallel('test_parallel', runs=5)
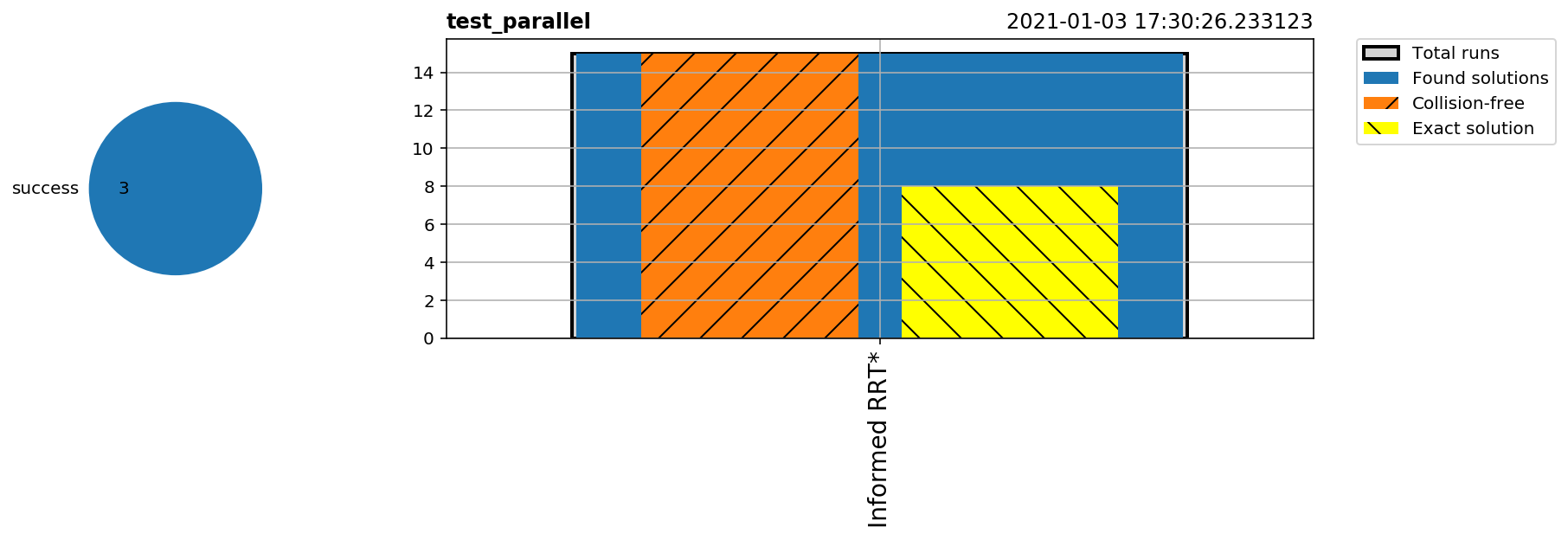
pool.visualize_trajectories(run_id='1')